
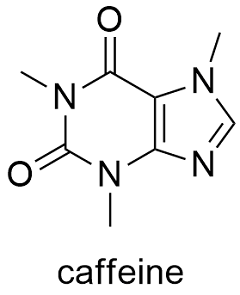
Caffeine molecule structure density and boiling point skin#
In dermatitis, caffeine lotions are supposed to apply to the skin to relieve redness and irritation.Sports personalities frequently use caffeine to be active, fast, and furious during their match time.
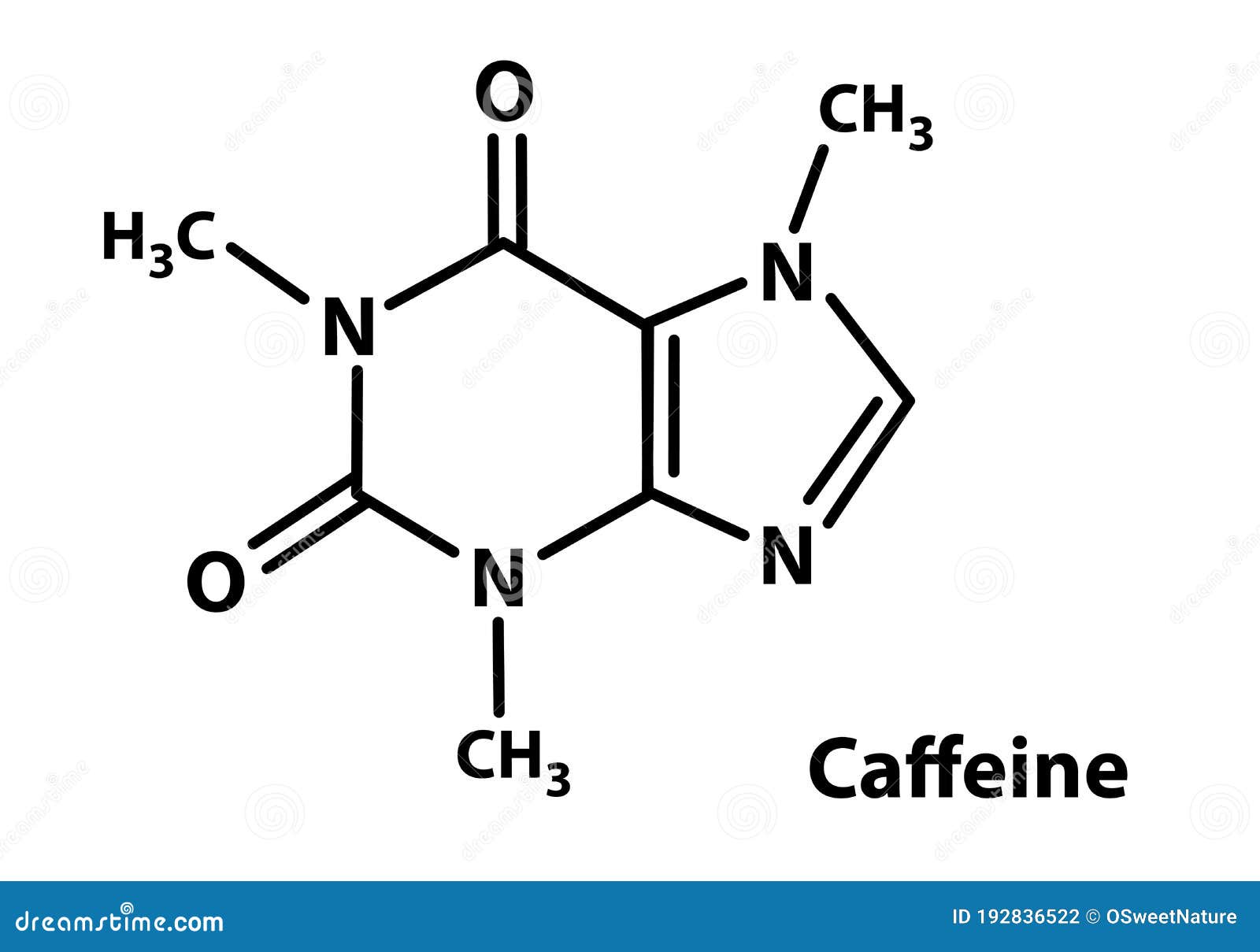
Since the structure of the caffeine molecule is very comparable to that of the adenosine molecule, especially the functions are equivalent to the nitrogen base adenine. The caffeine molecule can work in this way because its structure is remarkably similar to that of an adenosine molecule, especially where the nitrogen base adenine is concerned. The reaction implicated reversibly prevents adenosine's effect in specific receptors, causing the nervous system to be boosted. The molar mass of caffeine is 194.19 g/mol. It's a booster for the CNS (central nervous system). Caffeine is easily dissolved in water and liquids. It has a melting point of 235☌, a boiling point of 178 ☌. It has a harsh flavour and a density of 1.23 g mL1. The chemical names of caffeine are Trimethyl-xanthine, mateine, theine, guaranine, methyl theobromine. The reaction between dimethyl urea with malonic acid is one of these ways. In chemical laboratories, there are a few different ways to arrange caffeine. Caffeine dosage in tea and coffee is restricted to 5% to minimize addiction and bodily discomfort.Ĭaffeine is extracted utilizing organic solvents and a high-pressure extraction procedure to acquire the most significant amount of caffeine. It's a crystalline compound of whitish needles or powder, odourless, and hygroscopic. Physical PropertiesĬaffeine molecules are often derived from various plants grown explicitly for this function. The molecular formula for caffeine is C8H10N4O2.Caffeine is known by its IUPAC term of 1, 3, 7-Trimethylpurine-2,6-dione.A pyrimidinedione ring is a 6-member ring with two nitrogen atoms, whereas an imidazole ring is a 5-member ring with two nitrogen atoms. There are several techniques for producing caffeine, such as the coupling between dimethyl urea and malonic acid.Ĭaffeine is a pyrimidinedione and imidazole ring that has been bonded with each other to produce an alkaloid. Caffeine is limited to 5% in caffeine's product of tea and coffee to avoid addiction and discomforts in the body.Ĭaffeine is separated using solvents and a high extraction method. Xanthine is a purine base with a high protein content detected in living organism tissues.Ĭaffeine is generally derived from several plants that are farmed for this purpose. Methylxanthines, a chemical molecule derivative of xanthine, are found in caffeine. However, it may be synthesized in chemical labs and added to food or pharmaceuticals. It's also found in guarana seeds and yerba mate leaves. Caffeine is present in 16 distinct species, with coffee and tea plants. It is also a prominent booster and is a widely consumed beverage coffee component. It's an organic chemical on the World Health Organisation's list of the World's Most Needed Drugs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
